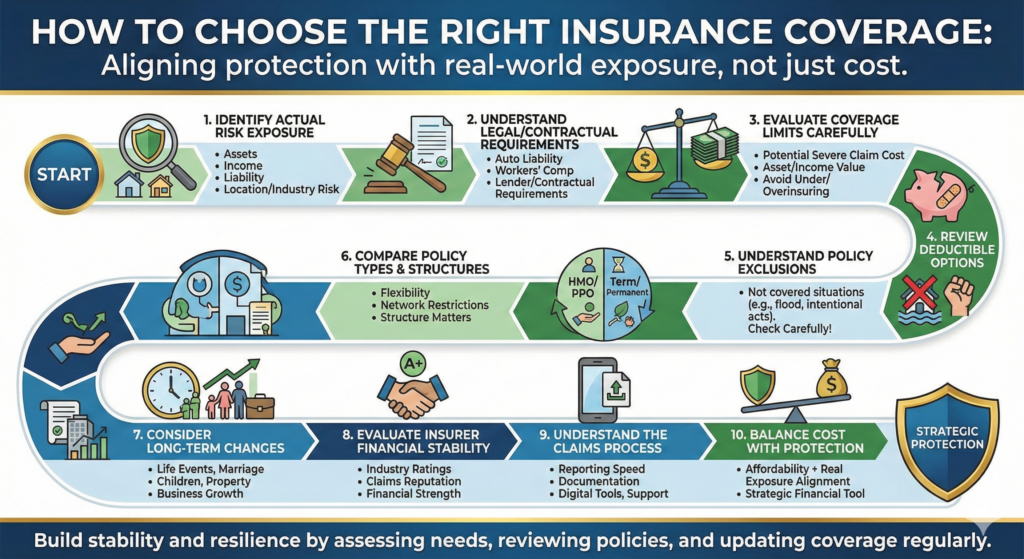
Choosing the right insurance coverage can feel overwhelming. With so many policy types, coverage limits, deductibles, and exclusions, it is easy to focus only on price. However, selecting insurance based solely on cost can result in gaps that create financial vulnerability later.
The purpose of insurance is not simply to meet legal requirements or satisfy contractual obligations. It is to manage financial risk in a structured and predictable way. Choosing the right insurance coverage means aligning protection with real-world exposure.
This guide explains how individuals and businesses can evaluate their needs and make informed insurance decisions.
Step 1: Identify Your Actual Risk Exposure
The first step in choosing insurance coverage is understanding what you are trying to protect.
Ask yourself:
- What assets do I own?
- What income do I rely on?
- What legal responsibilities do I have?
- What risks are most likely in my location or industry?
For individuals, risks may include:
- Auto accidents
- Property damage
- Medical expenses
- Loss of income
- Liability claims
For businesses, risks may extend to:
- Professional liability
- Cyber incidents
- Employee injuries
- Operational interruptions
Insurance decisions should be based on realistic exposure, not generalized assumptions.
Step 2: Understand Legal and Contractual Requirements
Certain types of insurance are required by law. For example:
- Auto liability insurance in most states
- Workers’ compensation for businesses with employees
Additionally, lenders, landlords, or clients may require specific coverage levels.
Meeting legal and contractual obligations is the baseline. However, minimum required coverage may not always reflect actual risk.
For example, minimum auto liability limits in some states may be insufficient in a serious accident.
Step 3: Evaluate Coverage Limits Carefully
Coverage limits define the maximum amount an insurer will pay for a covered claim.
Choosing limits requires considering:
- The potential cost of severe claims
- Asset value
- Income level
- Legal exposure
Underinsuring can result in out-of-pocket expenses that exceed policy limits. Overinsuring may increase premiums unnecessarily.
A balanced approach considers both affordability and realistic worst-case scenarios.
Step 4: Review Deductible Options
Deductibles represent the amount you must pay before insurance coverage applies.
Higher deductibles typically reduce premiums, while lower deductibles increase them.
When selecting a deductible, consider:
- Your emergency savings
- Your ability to absorb smaller losses
- Your tolerance for short-term financial impact
Choosing a deductible that aligns with your financial flexibility is critical.
Step 5: Understand Policy Exclusions
Insurance policies do not cover every possible event.
Exclusions define situations that are not covered. For example:
- Flood damage is often excluded from standard homeowners policies
- Intentional acts are typically excluded from liability coverage
- Certain professional services may require specialized policies
Carefully reviewing exclusions prevents misunderstandings during claims.
If a significant risk is excluded, additional coverage may be necessary.
Step 6: Compare Policy Types and Structures
Different policy structures may offer varying degrees of flexibility and cost-sharing.
For example:
- Health insurance plans differ in network restrictions
- Life insurance offers term and permanent options
- Disability insurance may define disability differently
Comparing policy structures helps ensure coverage matches personal or business needs.
Price comparison alone does not provide a complete picture.
Step 7: Consider Long-Term Changes
Insurance needs evolve over time.
Life events that may require policy review include:
- Marriage
- Having children
- Purchasing property
- Starting or expanding a business
- Significant income changes
Regularly reviewing insurance ensures coverage remains aligned with changing circumstances.
Insurance should adapt as responsibilities grow.
Step 8: Evaluate the Financial Stability of the Insurer
Insurance is a long-term contract. Selecting a reputable and financially stable insurer is important.
Factors to consider include:
- Industry ratings
- Customer service reputation
- Claims handling processes
- Regulatory standing
Reliable claims handling is one of the most important aspects of insurance value.
Step 9: Understand the Claims Process
Before purchasing a policy, it is helpful to understand how claims are handled.
Consider:
- How quickly claims must be reported
- Documentation requirements
- Available digital tools
- Customer support accessibility
Insurance provides value during claims. Clear processes reduce stress during difficult situations.
Step 10: Balance Cost with Protection
Affordability is important, but insurance should not be viewed purely as a cost-minimization decision.
The right insurance coverage:
- Protects against significant financial disruption
- Aligns with real exposure
- Fits within a sustainable budget
Choosing the lowest premium without evaluating coverage scope can create gaps that become costly later.
Personal Insurance vs. Business Insurance Considerations
Individuals typically focus on:
- Home insurance
- Auto insurance
- Health insurance
- Life and disability insurance
Businesses may require additional layers such as:
- General liability
- Professional liability
- Cyber insurance
- Commercial property coverage
Entrepreneurs and self-employed individuals should consider both personal and business exposure.
Separating personal and business insurance structures ensures clarity and protection.
The Role of Risk Assessment
Risk assessment involves evaluating the likelihood and severity of potential events.
For example:
- A homeowner in a flood-prone region may need additional coverage
- A technology startup handling customer data may require cyber insurance
- A consultant providing advice may need professional liability insurance
Risk assessment aligns insurance decisions with real-world exposure rather than generalized trends.
When to Seek Professional Advice
While many policies can be purchased online, complex situations may benefit from professional guidance.
Insurance advisors or brokers can help:
- Identify coverage gaps
- Compare multiple carriers
- Clarify policy language
- Customize coverage options
Expert guidance may be particularly helpful for business owners or individuals with unique assets.
Technology and Insurance Selection
Digital platforms now allow consumers to:
- Compare quotes
- Access policy details
- Adjust coverage limits
- Manage claims online
Technology improves transparency but does not replace the need for careful review.
Selecting insurance coverage remains a decision that requires thoughtful evaluation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When choosing insurance coverage, common mistakes include:
- Selecting minimum coverage without evaluating exposure
- Ignoring policy exclusions
- Failing to update policies after life changes
- Overlooking liability limits
- Choosing based solely on premium cost
Avoiding these mistakes improves long-term financial protection.
Conclusion
Choosing the right insurance coverage involves more than selecting a policy with an affordable premium. It requires evaluating risk exposure, understanding coverage limits and exclusions, and aligning protection with financial realities.
Insurance should be viewed as a strategic financial tool — one that protects income, assets, and legal exposure.
By carefully assessing needs, reviewing policy structures, and periodically updating coverage, individuals and businesses can build insurance strategies that provide stability and resilience in uncertain environments.
