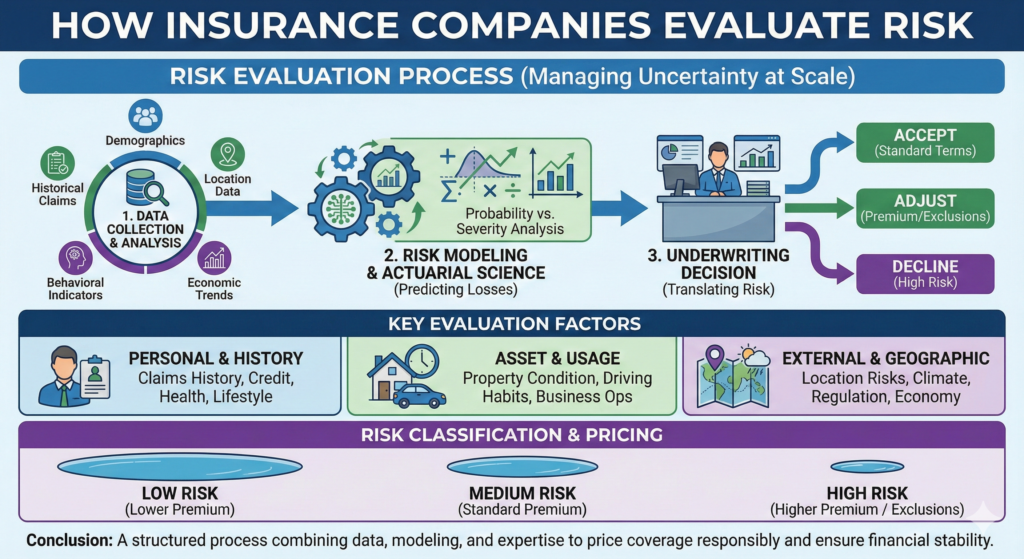
Risk evaluation is the foundation of the insurance industry. Every policy issued, every premium charged, and every coverage decision made by an insurance company is based on how risk is identified, measured, and managed. While most policyholders are aware that insurers “assess risk,” very few understand what that process actually involves.
Understanding how insurance companies evaluate risk helps explain why premiums differ between individuals, why coverage has limits, and why certain risks are excluded altogether. More importantly, it allows policyholders to make informed decisions and avoid common misunderstandings about how insurance works.
What Risk Means in Insurance
In insurance, risk refers to the likelihood that a loss will occur and the potential financial impact of that loss. Risk is not just about how often something might happen, but how costly it could be when it does.
Insurance companies evaluate risk by answering two fundamental questions:
- How likely is a loss to occur?
- How severe could that loss be?
Both probability and impact must be considered together. A risk that is unlikely but extremely costly may be treated very differently from a risk that occurs frequently but causes limited damage.
The Role of Data in Risk Evaluation
Data is the core resource used by insurance companies to evaluate risk. Insurers collect and analyze large volumes of information to identify patterns and trends that help predict future losses.
This data may include:
- Historical claims data
- Demographic information
- Geographic factors
- Behavioral indicators
- Industry-specific statistics
- Environmental and economic trends
By analyzing data across large populations, insurers can estimate how often certain events occur and how expensive they tend to be. This statistical approach allows insurers to price risk consistently and sustainably.
Actuarial Science and Risk Modeling
Actuarial science plays a central role in insurance risk evaluation. Actuaries use mathematical and statistical methods to model uncertainty and forecast future claims.
These models help insurers:
- Estimate expected losses
- Set appropriate premium levels
- Determine coverage limits
- Maintain financial stability
Actuarial models are continuously refined as new data becomes available. This ongoing process helps insurers adapt to changes in behavior, technology, and external conditions.
Underwriting: Translating Risk Into Decisions
Underwriting is the process through which risk evaluation is translated into real-world decisions. Underwriters review information about an applicant and determine whether to offer coverage, under what terms, and at what price.
Underwriting decisions may involve:
- Accepting the risk as standard
- Adjusting premiums based on risk factors
- Applying exclusions or endorsements
- Declining coverage for certain risks
Underwriters must balance competitiveness with caution. Pricing risk too low can threaten an insurer’s financial health, while pricing too high can make coverage inaccessible.
Key Factors Insurance Companies Consider
While risk evaluation varies by type of insurance, several common factors are often considered.
Personal and Demographic Factors
Age, occupation, health indicators, and lifestyle factors may influence risk in personal insurance lines.
Geographic Location
Location affects exposure to natural disasters, crime rates, traffic patterns, and regulatory environments.
Behavior and Usage Patterns
How something is used often matters as much as what it is. Driving habits, property maintenance, or business operations can all influence risk.
Claims History
Past claims are one of the strongest indicators of future risk. Frequent or severe claims often lead to higher premiums or coverage restrictions.
Risk Classification and Pooling
Once risks are evaluated, insurers classify policyholders into groups with similar risk profiles. This process allows insurers to pool risks efficiently and price coverage fairly within each group.
Risk classification is essential for maintaining balance within the insurance system. Without it, lower-risk individuals would subsidize higher-risk ones disproportionately, potentially destabilizing the pool.
Classification does not eliminate individual differences, but it allows insurers to manage risk at scale.
The Role of Technology in Risk Evaluation
Technology has transformed how insurance companies evaluate risk. Advanced analytics, automation, and artificial intelligence allow insurers to process information faster and more accurately than ever before.
Modern systems can:
- Analyze large datasets in real time
- Detect patterns that humans might miss
- Adjust pricing dynamically
- Improve fraud detection
While technology improves efficiency, it also raises important questions about transparency and data usage. Regulators continue to monitor how automated systems influence insurance decisions.
External Risk Factors and Uncertainty
Not all risks can be fully predicted. Economic changes, climate trends, legal developments, and global events can all affect loss patterns.
Insurance companies account for this uncertainty by:
- Maintaining capital reserves
- Diversifying risk portfolios
- Reinsuring portions of their exposure
These strategies help insurers remain resilient even when unexpected events occur.
Why Some Risks Are Excluded
Certain risks are excluded from insurance coverage because they are too unpredictable, too widespread, or too costly to insure sustainably.
Exclusions are not arbitrary. They exist to protect the integrity of the insurance system. Without exclusions, premiums would rise dramatically, and coverage would become inaccessible for many policyholders.
Understanding exclusions helps explain the limits of what insurance can realistically provide.
Risk Evaluation and Regulation
Insurance risk evaluation operates within a regulatory framework. Regulators ensure that insurers use fair, non-discriminatory practices and remain financially solvent.
Regulation plays a critical role in maintaining trust between insurers and policyholders. It ensures that risk evaluation supports long-term stability rather than short-term profit.
Why Risk Evaluation Matters to Policyholders
For policyholders, understanding risk evaluation provides valuable insight into how insurance decisions are made.
It helps explain:
- Why premiums vary
- Why coverage has limits
- Why certain information is requested
- Why policies change over time
This understanding reduces frustration and encourages more informed engagement with insurance products.
Conclusion
Insurance companies evaluate risk through a structured process that combines data, statistical modeling, underwriting expertise, and regulatory oversight. This process allows insurers to price coverage responsibly and remain financially stable over time.
Risk evaluation is not about predicting individual outcomes, but about managing uncertainty across large populations. By understanding how this process works, policyholders can make better decisions and appreciate the role insurance plays in managing risk in an uncertain world.
