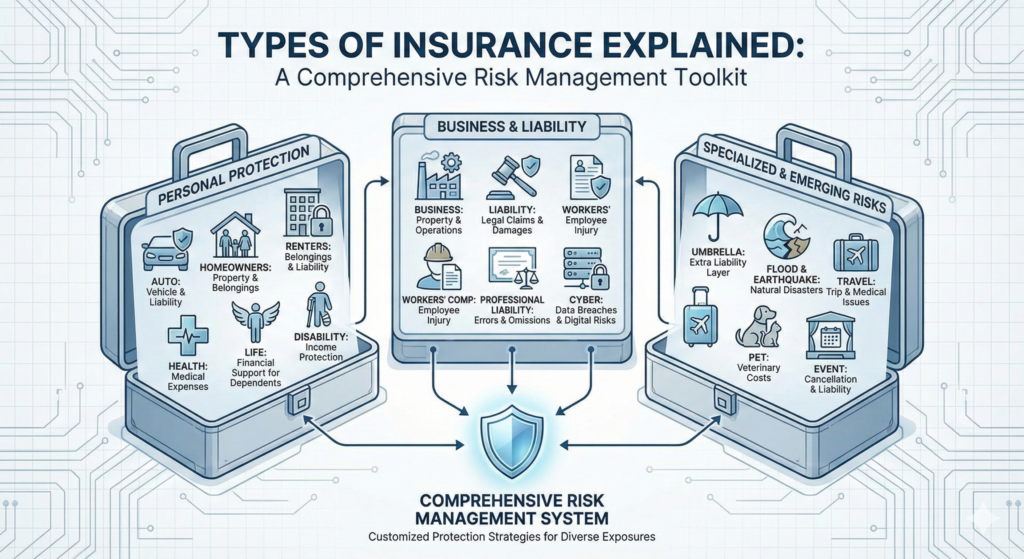
Insurance is not a single product. It is a broad category of financial protection designed to address many different types of risk. While the basic concept of insurance remains the same — transferring financial risk in exchange for a premium — the way it is applied varies significantly depending on what is being protected.
Understanding the different types of insurance is essential for making informed decisions. Each type exists for a specific reason and addresses a particular category of exposure. Some forms of insurance are legally required, while others are optional but highly recommended depending on personal or business circumstances.
This guide explains the most common types of insurance in the United States and how they function within the broader risk management system.
Auto Insurance
Auto insurance is one of the most widely recognized and commonly required forms of insurance in the United States. Most states require drivers to carry minimum liability coverage.
Auto insurance typically includes:
- Liability coverage, which pays for injuries or property damage caused to others
- Collision coverage, which pays for damage to your own vehicle after an accident
- Comprehensive coverage, which protects against non-collision events such as theft, vandalism, or natural disasters
- Uninsured or underinsured motorist coverage, which protects against drivers who lack sufficient insurance
Auto insurance is designed not only to protect vehicles but also to manage legal responsibility in the event of an accident.
Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance protects residential property and personal belongings. It also provides liability coverage if someone is injured on the property.
A typical homeowners policy includes:
- Coverage for the physical structure of the home
- Protection for personal property inside the home
- Liability coverage for accidents
- Additional living expenses if the home becomes temporarily uninhabitable
It is important to distinguish between market value and replacement cost when evaluating home insurance. Coverage is generally based on the cost to rebuild, not the property’s resale value.
Renters Insurance
Renters insurance is designed for individuals who do not own their residence. While the landlord’s insurance covers the building itself, renters insurance protects personal belongings and provides liability coverage.
This type of insurance is often affordable and can protect against theft, fire, or certain types of property damage. It also includes personal liability protection, which can be important even for tenants.
Health Insurance
Health insurance helps cover medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription medications, and preventive care.
In the United States, healthcare costs can be significant, making health insurance essential for managing financial exposure. Policies may include deductibles, co-payments, and out-of-pocket maximums.
Health insurance may be obtained through employers, government programs, or private marketplaces.
Life Insurance
Life insurance provides financial support to beneficiaries after the death of the insured person. It is commonly used to replace income, pay debts, or support dependents.
There are two primary types:
- Term life insurance, which provides coverage for a specific period
- Permanent life insurance, which remains in force for the insured’s lifetime and may include a savings component
Life insurance is particularly important for individuals with financial dependents.
Disability Insurance
Disability insurance protects income if a person becomes unable to work due to illness or injury.
Since earning ability is often a person’s most valuable financial asset, disability insurance plays a critical role in long-term financial planning. Coverage may be short-term or long-term, depending on the policy.
This type of insurance helps maintain financial stability during periods of unexpected health-related disruption.
Business Insurance
Businesses face a wide range of risks, including property damage, lawsuits, employee injuries, and operational interruptions.
Business insurance may include:
- General liability insurance
- Property insurance
- Workers’ compensation insurance
- Professional liability insurance
- Business interruption coverage
Business insurance helps companies remain operational after unexpected events and is often required by law or contract.
Liability Insurance
Liability insurance protects against legal claims resulting from injury or damage to others. It is a critical component of both personal and commercial insurance policies.
Examples include:
- Personal liability coverage in homeowners policies
- Professional liability insurance for licensed professionals
- Commercial general liability insurance for businesses
In a legal environment where claims can result in significant financial consequences, liability insurance provides essential protection.
Umbrella Insurance
Umbrella insurance provides additional liability coverage beyond the limits of standard policies such as auto or homeowners insurance.
It acts as a secondary layer of protection and is often used by individuals seeking higher liability limits to protect assets.
Umbrella policies are designed to address large, unexpected claims that exceed primary coverage limits.
Cyber Insurance
Cyber insurance has become increasingly important as digital risks grow. This type of insurance helps cover losses related to data breaches, cyberattacks, and other digital security incidents.
Coverage may include:
- Data recovery costs
- Legal expenses
- Regulatory fines (where permitted)
- Business interruption due to cyber incidents
Cyber insurance is particularly relevant for businesses that store or process sensitive information.
Travel Insurance
Travel insurance provides coverage for trip cancellations, medical emergencies abroad, lost luggage, and other travel-related disruptions.
While not always required, travel insurance can provide financial protection during international travel or high-cost trips.
Specialty Insurance
Specialty insurance covers unique or high-risk situations. Examples include:
- Flood insurance
- Earthquake insurance
- Event insurance
- Pet insurance
- Professional malpractice insurance
These policies address specific risks not typically covered under standard policies.
How to Determine Which Types You Need
The types of insurance an individual or business needs depend on several factors:
- Legal requirements
- Asset ownership
- Income stability
- Business operations
- Risk exposure
Rather than purchasing every available policy, it is important to assess potential financial impact and prioritize coverage accordingly.
Why Insurance Types Continue to Evolve
Insurance evolves as society changes. New risks emerge from technological advancement, environmental trends, and economic shifts.
For example:
- Cyber insurance developed in response to digital threats
- Climate-related coverage options have expanded in response to environmental changes
As risk landscapes evolve, so do the types of insurance designed to manage them.
Conclusion
Insurance exists in many forms, each tailored to address specific risks. From auto and homeowners insurance to business and cyber coverage, each type serves a distinct purpose within the broader risk management system.
Understanding the different types of insurance empowers individuals and businesses to make informed decisions and build comprehensive protection strategies. Rather than viewing insurance as a single product, it is more accurate to see it as a toolkit — one that must be customized to fit individual circumstances and exposure levels.
